Ethereum is celebrated as the premier blockchain platform, noted for its powerful smart contracts and expansive ecosystem of decentralized applications (DApps). Yet, its extensive use brings about scalability challenges that affect its seamless interaction with other blockchain networks. The solution to these challenges lies in “What are Ethereum Bridges?”—they are pivotal technologies that enable the free flow of assets and data across Ethereum and various other blockchain systems, effectively solving interoperability issues.
What are Ethereum Bridges?

Ethereum bridges typically refer to specialized protocols that are engineered to forge connections between the Ethereum blockchain and other blockchain networks. These bridges facilitate the transfer of digital assets, data, and even functional capabilities across blockchain boundaries, effectively linking disparate ecosystems. This connectivity allows users to access a broader array of DApps and services, transcending the limitations imposed by single blockchain infrastructures.
Types of Ethereum Bridges
There are primarily two categories of Ethereum bridges, each serving unique needs within the blockchain landscape:
-
Trustless Bridges: These bridges operate on smart contracts that autonomously execute and secure asset transfers without the need for intermediaries, adhering to the decentralized nature of blockchain technology.
-
Centralized Bridges: These rely on intermediaries or trusted third parties to manage and validate cross-chain transactions. While they often offer faster transaction speeds, they provide a less decentralized approach compared to trustless bridges.
Both types of bridges are pivotal in addressing the interoperability and scalability challenges faced by the Ethereum network, enabling more efficient interactions across diverse blockchain ecosystems.
How Do Ethereum Bridges Work?
Ethereum bridges function by locking assets on the original blockchain (source) and subsequently minting equivalent tokens on the target blockchain (destination). Here’s a breakdown of the process:
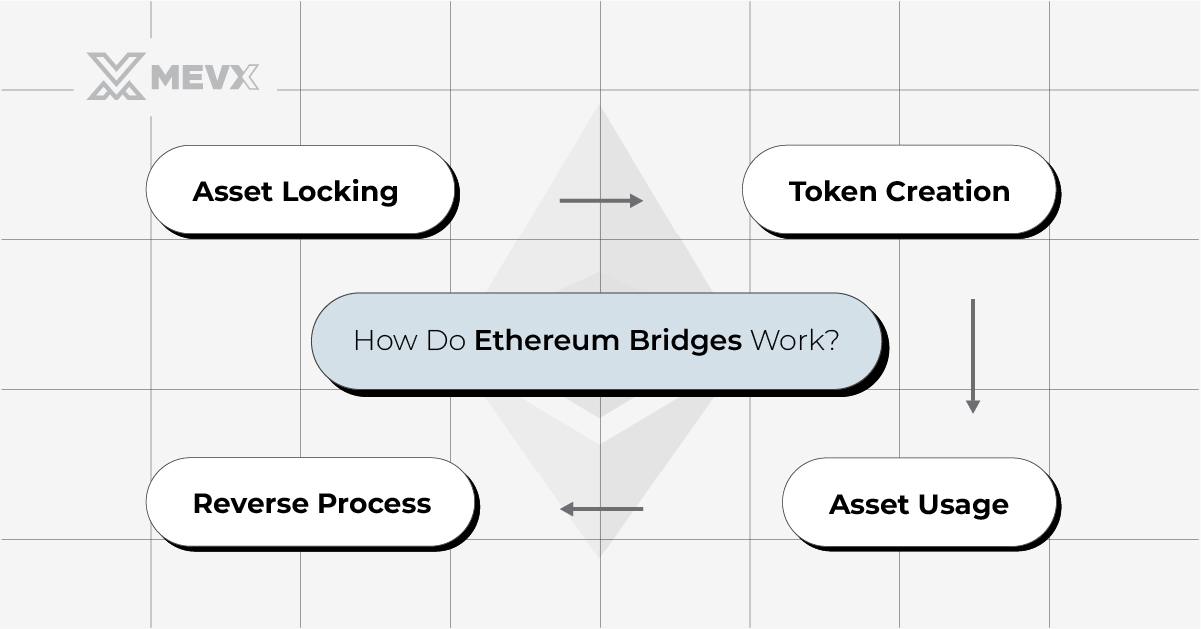
- Asset Locking: Users initiate the process by transferring assets to a designated smart contract on the source blockchain, where the assets are securely locked.
- Token Minting: The bridge protocol then mints tokens on the destination blockchain that are equivalent in value to the locked assets.
- Asset Utilization: These newly minted tokens can be freely used for transactions or within DApps on the destination blockchain.
- Reverse Process: To retrieve the original assets, the minted tokens are burnt on the destination blockchain, unlocking the equivalent value on the source blockchain.
This mechanism enhances the fluidity of asset movement across different blockchain platforms.
Benefits of Ethereum Bridges
- Interoperability: Bridges expand the reach of Ethereum-based DApps and services to other blockchains, enhancing the overall utility of the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Scalability: By distributing transactions across multiple blockchains, bridges help alleviate congestion on the Ethereum network and reduce transaction costs (gas fees).
- Enhanced Liquidity: Smooth asset transfers between networks improve market liquidity and facilitate diversified investment opportunities.
- Developer Innovation: The ability to integrate applications across different blockchains fosters innovation, paving the way for advanced blockchain applications and use cases.
Examples of Prominent Ethereum Bridges
Several notable Ethereum bridges have emerged, each offering unique functionalities:
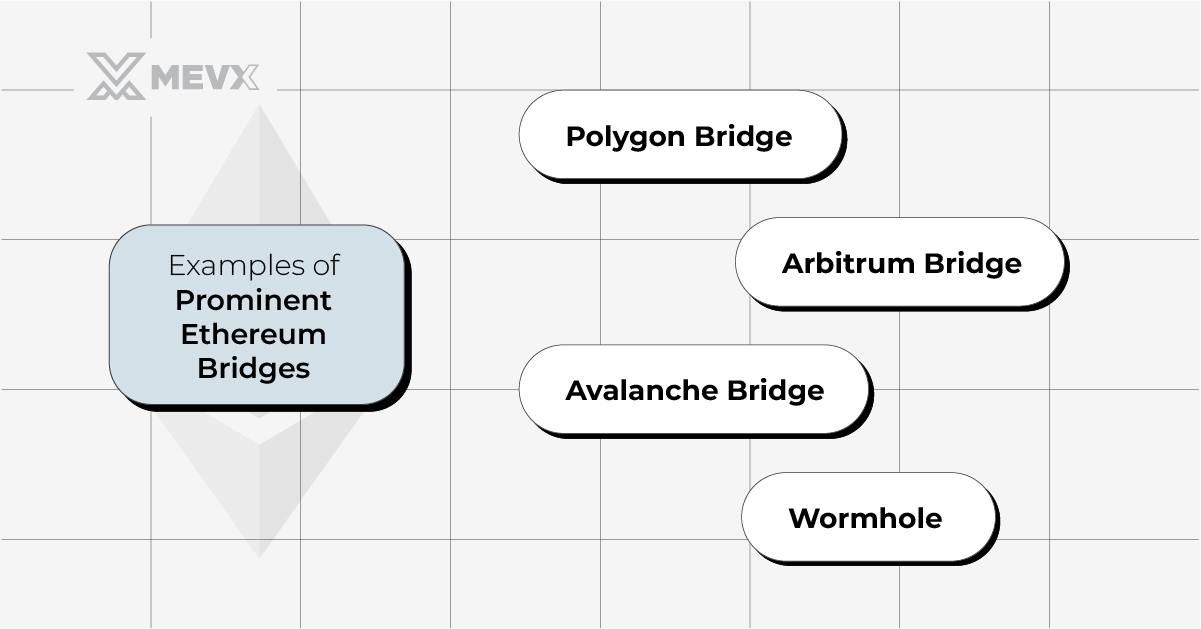
- Polygon Bridge: This Layer-2 solution enhances the scalability of Ethereum by enabling fast, cost-effective transfers between the Ethereum and Polygon networks.
- Arbitrum Bridge: Utilizes optimistic roll-ups to increase transaction throughput without compromising on security.
- Avalanche Bridge: Facilitates swift and economical transfers between Ethereum and the Avalanche network.
- Wormhole: Supports transfers of various token standards, including NFTs, between Ethereum and other major blockchains like Solana.
Challenges and Risks
While Ethereum bridges bring numerous advantages, they also introduce certain risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Flaws in bridge contracts can lead to significant asset losses.
- Centralization Risks: Centralized bridges may suffer from points of failure and potential censorship issues.
- Cross-Chain Attacks: Vulnerabilities in one network could endanger assets across connected networks.
Mitigating these risks involves using reputable bridges and adhering to best security practices to protect user assets.
Why Do Ethereum Bridges Matter?
Ethereum bridges are crucial for enhancing interoperability within the blockchain domain, addressing scalability issues, and facilitating broader access to blockchain applications. As blockchain technology evolves, these bridges are poised to play an integral role in fostering a cohesive and efficient decentralized ecosystem.
In conclusion, Ethereum bridges are more than mere technical solutions; they are vital components that drive connectivity and scalability across the blockchain world, heralding a future of seamless inter-blockchain cooperation and innovation.
